Subformulario
Un subformulario es un formulario incluido en otro formulario.
Terminología
Con el fin de definir claramente los conceptos implementados con los subformularios, aquí hay algunas definiciones para ciertos términos utilizados:
- Subformulario: un formulario destinado a ser incluido en otro formulario, llamado a su vez formulario padre.
- Formulario padre: un formulario que contiene uno o más subformularios.
- Contenedor de subformulario: un objeto incluido en el formulario padre, que muestra una instancia del subformulario.
- Instancia de subformulario: la representación de un subformulario en un formulario padre. Este concepto es importante porque es posible mostrar varias instancias del mismo subformulario en un formulario padre.
- Formulario listado: instancia de subformulario mostrada como una lista.
- Formulario detallado: formulario de entrada tipo página asociado a un subformulario tipo lista al que se accede haciendo doble clic en la lista.
Sub-formularios en lista
Un subformulario lista le permite introducir, ver y modificar datos en otras tablas. Normalmente se utilizan subformularios lista en bases de datos en las que se han establecido relaciones Uno a Muchos. Un subformulario lista en un formulario de una tabla Uno relacionada le permite ver, introducir y modificar datos en una tabla Muchos relacionada. Puede tener varios subformularios procedentes de diferentes tablas en el mismo formulario. Sin embargo, no es posible colocar dos subformularios que pertenecen a la misma tabla en la misma página de un formulario.
Por ejemplo, una base de datos del gestor de contactos puede utilizar un subformulario lista para mostrar todos los números de teléfono de un contacto. Aunque los números de teléfono aparecen en la pantalla Contactos, la información se almacena realmente en una tabla relacionada. Utilizando una relación de Uno a Muchos, este diseño de base de datos facilita el almacenamiento de un número ilimitado de números de teléfono por contacto. Con las relaciones automáticas, se puede soportar la entrada de datos directamente en la tabla Muchos relacionada sin programar.
Aunque los subformularios lista suelen estar asociados a muchas tablas, una instancia de subformulario puede mostrar los registros de cualquier otra tabla de la base de datos.
También puede permitir que el usuario introduzca datos en el formulario lista. Dependiendo de la configuración del subformulario, el usuario puede mostrar el formulario detallado haciendo doble clic en un subregistro o utilizando los comandos para añadir y editar subregistros.
4D ofrece tres acciones estándar para satisfacer las necesidades básicas de gestión de los subregistros:
Edit Subrecord,Delete SubrecordyAdd Subrecord. Cuando el formulario incluye varias instancias de subformulario, la acción se aplicará al subformulario que tenga el foco.
Sub-formularios en página
Los subformularios en modo página pueden mostrar los datos del subregistro actual o todo valor pertinente en función del contexto (variables, imágenes, etc.). Una de las principales ventajas de utilizar subformularios página es que pueden incluir funcionalidades avanzadas y pueden interactuar directamente con el formulario padre (widgets). Los subformularios en página también tienen sus propiedades y eventos específicos; puede gestionarlos completamente por programación.
El subformulario en página utiliza el formulario de entrada indicado por la propiedad Formulario detallado. A diferencia de un subformulario en modo lista, el formulario utilizado puede proceder de la misma tabla que el formulario padre. También es posible utilizar un formulario proyecto. Cuando se ejecuta, un subformulario en modo página tiene las mismas características de visualización estándar que un formulario de entrada.
Los widgets 4D son objetos compuestos predefinidos basados en subformularios página. Se describen detalladamente en un manual aparte, 4D Widgets.
Utilización de la variable o expresión asociada
Puede vincular una variable o una expresión a un objeto contenedor de subformulario. Esto es muy útil para sincronizar valores del formulario padre y su(s) subformulario(s).
Por defecto, 4D crea una variable o expresión de tipo objeto para un contenedor de subformulario, lo cual le permite compartir valores en el contexto del subformulario utilizando el comando Form. Sin embargo, puede utilizar una variable o expresión de cualquier tipo escalar (tiempo, entero, etc.) especialmente si sólo necesita compartir un único valor:
- Defina una variable ligada o una expresión de tipo escalar y llame a los comandos
OBJECT Get subform container valueyOBJECT SET SUBFORM CONTAINER VALUEpara intercambiar valores cuando se produzcan los eventos de formulario On Bound Variable Change o On Data Change. Esta solución se recomienda para sincronizar un solo valor. - Defina una variable o expresión vinculada del tipo objecto y utilice el comando
Formpara acceder a sus propiedades desde el subformulario. Esta solución se recomienda para sincronizar varios valores.
Sincronizando formulario padre y subformulario (valor único)
Vincular la misma variable o expresión al contenedor del subformulario y a otros objetos del formulario principal permite vincular los contextos del formulario principal y del subformulario para dar los toques finales a interfaces sofisticadas. Imagine un subformulario que contiene un reloj que muestra una hora estática, insertado en un formulario padre que contiene un área de entrada:
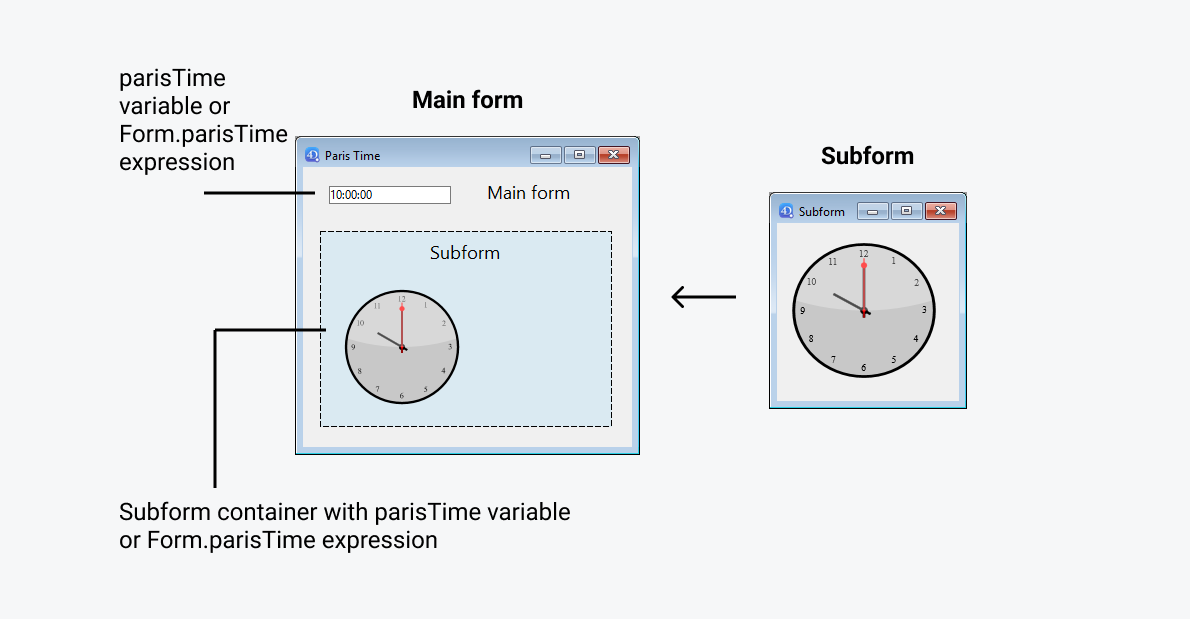
En el formulario padre, ambos objetos (área de entrada y contenedor subformulario) tienen el mismo valor que Variable o Expresión. Puede ser una variable (por ejemplo, parisTime), o una expresión (por ejemplo, Form.parisTime).
Para mostrar una hora estática, debe utilizar el tipo de datos apropiado para la variable o la expresión:
- Si utiliza una variable (por ejemplo,
parisTime), debe ser del tipotextootiempo. - Si utiliza una expresión (por ejemplo,
Form.myValue), debe contener un valortexto.
El valor del texto debe tener el formato "hh:mm:ss".
En el subformulario, el objeto reloj se gestiona a través de la propiedad Form.clockValue.
Actualizando el contenido de un subformulario
Caso 1: se modifica el valor de la variable o expresión del formulario padre y esta modificación debe pasarse al subformulario.
parisTime o Form.parisTime cambia a "12:15:00" en el formulario padre, bien porque el usuario lo ha introducido, bien porque se ha actualizado dinámicamente (a través de la sentencia String(Current time) por ejemplo). Esto activa el evento On Bound Variable Change en el método formulario del subformulario.
Se ejecuta el siguiente código:
// Método de formulario del subformulario
If (Form event code=On Bound Variable Change) //la variable o expresión vinculada se modificó en el formulario padre
Form.clockValue:=OBJECT Get subform container value //sincroniza el valor local
End if
Actualiza el valor de Form.clockValue en el subformulario:
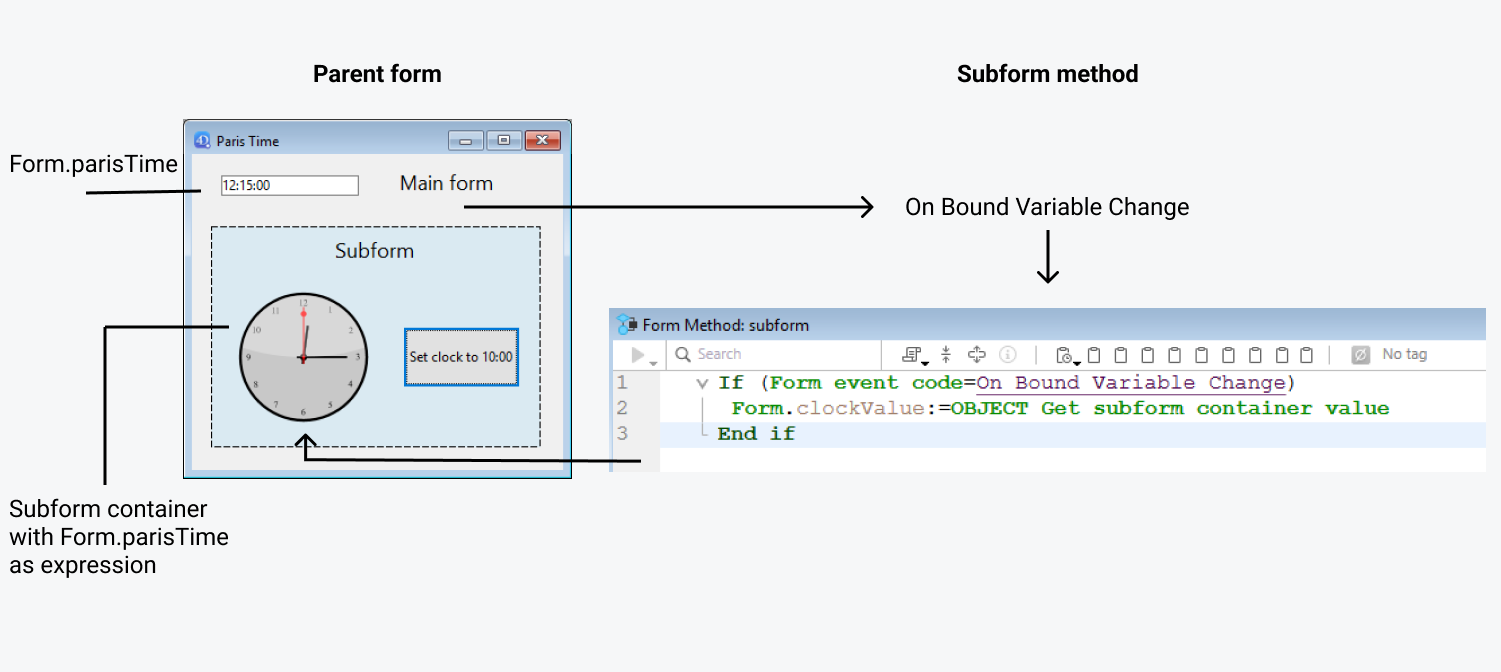
Se genera el evento formulario On Bound Variable Change:
- en cuanto se asigna un valor a la variable/expresión del formulario padre, incluso si se reasigna el mismo valor
- si el subformulario pertenece a la página formulario actual o a la página 0.
Tenga en cuenta que, como en el ejemplo anterior, es preferible utilizar el comando OBJECT Get subform container value que devuelve el valor de la expresión en el contenedor del subformulario en lugar de la propia expresión, ya que es posible insertar varios subformularios en el mismo formulario padre (por ejemplo, una ventana que muestra diferentes zonas horarias contiene varios relojes).
La modificación de la variable o expresión asociada desencadena eventos de formulario que permiten sincronizar los valores del formulario padre y del subformulario:
- Utilice el evento de formulario On Bound Variable Change para indicar al subformulario (método de formulario del subformulario) que la variable o expresión fue modificada en el formulario padre.
- Utilice el evento de formulario On Data Change para indicar al contenedor del subformulario que el valor de la variable o expresión fue modificado en el subformulario.
Actualizar el contenido de un formulario padre
Caso 2: se modifica el contenido del subformulario y esta modificación debe pasar al formulario padre.
Dentro del subformulario, el botón cambia el valor de la expresión Form.clockValue de tipo Text asociada al objeto reloj. Esto activa el evento de formulario On Data Change dentro del objeto reloj (este evento debe estar seleccionado para el objeto), que actualiza el valor Form.parisTime en el formulario principal.
Se ejecuta el siguiente código:
// método objeto subform clock
If (Form event code=On Data Change) //sea cual sea la forma de cambiar el valor
OBJECT SET SUBFORM CONTAINER VALUE(Form.clockValue) //Empujar el valor al contenedor
End if
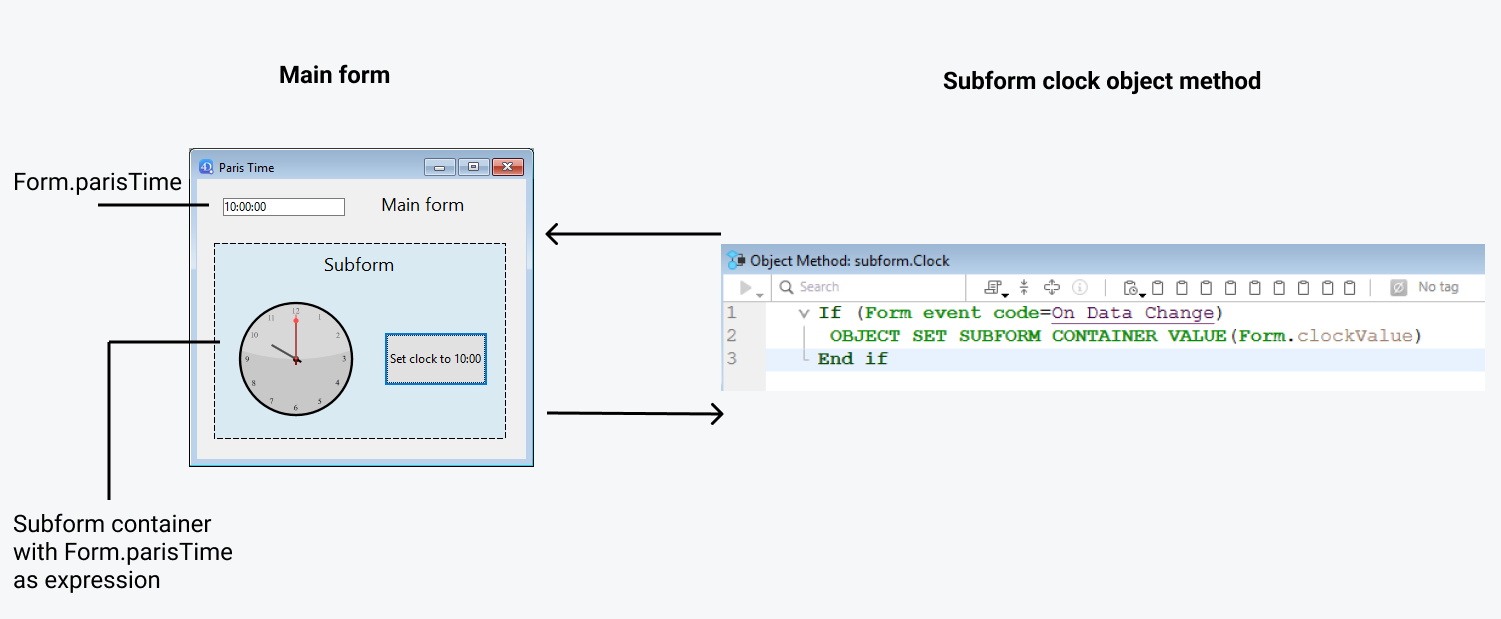
Cada vez que cambia el valor de Form.clockValue en el subformulario, también se actualiza parisTime o Form.parisTime en el contenedor del subformulario.
Si el valor de la variable o expresión se establece en varias ubicaciones, 4D utiliza el valor que se cargó en último lugar. Aplica el siguiente orden de carga: 1-Métodos objeto del subformulario, 2-Método formulario del subformulario, 3-Métodos objeto del formulario padre, 4-Método formulario del formulario padre
Sincronizando formulario padre y subformulario (múltiples valores)
Por defecto, 4D vincula una variable o expresión de tipo de objeto a cada subformulario. El contenido de este objeto puede leerse y/o modificarse desde el formulario padre y desde el subformulario, lo que permite compartir múltiples valores en un contexto local.
Cuando se asocia al contenedor del subformulario, este objeto es devuelto por el comando Form directamente en el subformulario. Dado que los objetos se pasan siempre por referencia, si el usuario modifica el valor de una propiedad en el subformulario, se guardará automáticamente en el propio objeto y, por tanto, estará disponible para el formulario padre. Por otro lado, si una propiedad del objeto es modificada por el usuario en el formulario padre o por programación, se actualizará automáticamente en el subformulario. No es necesaria ninguna gestión de eventos.
Por ejemplo, en un subformulario, las entradas están vinculadas a las propiedades del objeto Form (del formulario del subformulario):
En el formulario padre, se muestra el subfomulario dos veces. Cada contenedor de subformulario está asociado a una expresión que es una propiedad del objeto Form (del formulario padre):
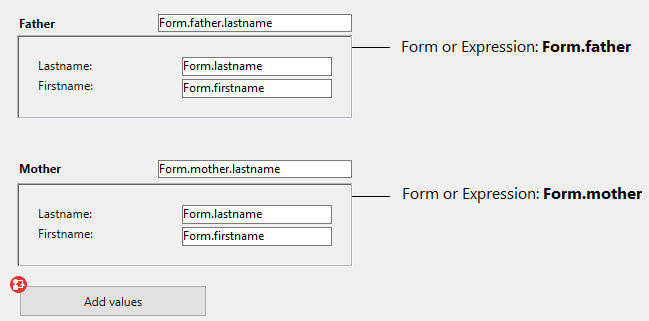
El botón sólo crea las propiedades mother y father en el objeto Form del padre:
//Método objeto botón añadir valores
Form.mother:=New object("lastname"; "Hotel"; "firstname"; "Anne")
Form.father:=New object("lastname"; "Golf"; "firstname"; "Félix")
Cuando ejecuta el formulario y presiona el botón, ve que todos los valores se muestran correctamente:
Si modifica un valor en el formulario padre o en el subformulario, se actualiza automáticamente en el otro formulario porque se utiliza el mismo objeto:
Uso de punteros (compatibilidad)
En versiones anteriores a 4D v19 R5, la sincronización entre formularios padre y subformularios se gestionaba a través de punteros. Por ejemplo, para actualizar un objeto subformulario, podría llamar al siguiente código:
// Método subformulario
If (Form event code=On Bound Variable Change)
ptr:=OBJECT Get pointer(Object subform container)
clockValue:=ptr->
End if
Este principio aún se soporta por compatibilidad, pero ahora es obsoleto, ya que no permite vincular expresiones a subformularios. Ya no debería utilizarse en sus desarrollos. En todos los casos, recomendamos utilizar el comando Form o los comandos OBJECT Get subform container value y OBJECT SET SUBFORM CONTAINER VALUE para sincronizar los valores de formulario y subformulario.
Programación entre formularios avanzada
La comunicación entre el formulario padre y las instancias del subformulario puede requerir ir más allá del intercambio de valores a través de la variable asociada. De hecho, es posible que desee actualizar las variables de los subformularios en función de las acciones realizadas en el formulario principal y viceversa. Si utilizamos el ejemplo anterior del subformulario de tipo "reloj dinámico", es posible que queramos definir una o varias horas de alarma para cada reloj.
4D ha implementado los siguientes mecanismos para satisfacer estas necesidades:
- Llamada de un objeto contenedor desde el subformulario utilizando el comando
CALL SUBFORM CONTAINER - Ejecución de un método en el contexto del subformulario mediante el comando
EXECUTE METHOD IN SUBFORM
El comando
GOTO OBJECTbusca el objeto de destino en el formulario padre aunque se ejecute desde un subformulario.
Comando CALL SUBFORM CONTAINER
El comando CALL SUBFORM CONTAINER permite que una instancia de subformulario envíe un evento al objeto contenedor del subformulario, que puede procesarlo en el contexto del formulario padre. El evento se recibe en el método del objeto contenedor. Puede estar en el origen de todo evento detectado por el subformulario (clic, arrastrar y soltar, etc.).
El código del evento no tiene restricciones (por ejemplo, 20000 o -100). Puede utilizar un código que corresponda a un evento existente (por ejemplo, 3 para On Validate), o utilizar un código personalizado. En el primer caso, sólo puede utilizar los eventos que haya marcado en la lista de propiedades para los contenedores de subformulario. En el segundo caso, el código no debe corresponder a ningún evento de formulario existente. Se recomienda utilizar un valor negativo para asegurarse de que este código no será utilizado por 4D en futuras versiones.
Para más información, consulte la descripción del comando CALL SUBFORM CONTAINER.
Comando EXECUTE METHOD IN SUBFORM
El comando EXECUTE METHOD IN SUBFORM permite que un formulario o uno de sus objetos solicite la ejecución de un método en el contexto de la instancia del subformulario, lo que le da acceso a las variables, objetos, etc. del subformulario. Este método también puede recibir parámetros.
Este mecanismo se ilustra en el siguiente diagrama:
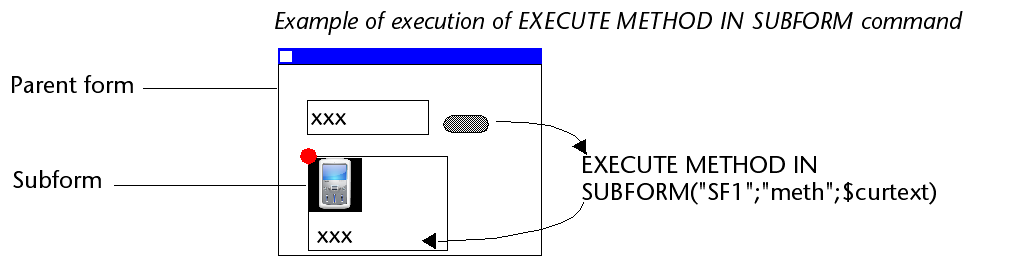
Para más información, consulte la descripción del comando EXECUTE METHOD IN SUBFORM.
Propiedades soportadas
Estilo de Borde - Inferior - Clase - Formulario detallado - Doble clic en fila vacía - Doble clic en fila - Editable en lista - Tipo de expresión - Enfocable - Altura - Ocultar rectángulo de enfoque - Barra de desplazamiento horizontal - Dimensionado horizontal - Izquierda - Formulario listado - Método - Nombre de objeto - Marco de impresión - Derecha - Modo de selección - Fuente - Superior - Tipo - Variable o Expresión - Barra de desplazamiento vertical - Dimensionado vertical - Visibilidad - Ancho