4D-SVG
SVG_PATH_ARC
SVG_PATH_ARC ( parentSVGObject ; xRadius ; yRadius ; x ; y {; rotation {; arcpath}} )
| Parameter | Type | Description | |
|---|---|---|---|
| parentSVGObject | SVG_Ref | → | Reference of path element |
| xRadius | Longint | → | Radius of ellipse on X axis |
| yRadius | Longint | → | Radius of ellipse on Y axis |
| x | Longint | → | Coordinate on X axis of destination point |
| y | Longint | → | Coordinate on Y axis of destination point |
| rotation | Longint | → | Value of rotation |
| arcpath | Longint | → | Sets the way the arc will be drawn |
Description
The SVG_PATH_ARC command draws an elliptical arc, from the current point to the point (x, y), at the end of the path referenced by parentSVGObject. If parentSVGObject is not a path reference (‘path’ element), an error is generated.
The size and orientation of the ellipse are set by two radii (xRadius, yRadius) and a rotation value on the X axis that indicates the rotation of the ellipse as a whole with respect to the current coordinate system.
The optional arcpath parameter can be used to apply a combination of constraints which will determine how the arc will be drawn. The large-arc-flag constraint is used to choose (or not) the larger of the two possible arcs (greater than 180°) and the sweep-flag constraint chooses the direction it will be drawn (positive angle or negative angle).
The following values, representing the four possible combinations of the two constraints, can be passed:
- 0: large-arc-flag = 0, sweep-flag = 1
- 1: large-arc-flag = 1, sweep-flag = 0
- 2: large-arc-flag = 0, sweep-flag = 0
- 3: large-arc-flag = 1, sweep-flag = 1
When large-arc-flag is equal to 1, the larger arc is drawn (and the smaller when it is equal to 0). When sweep-flag is equal to 1, the arc is drawn at a positive angle (and at a negative angle when it is equal to 0).
The following drawing illustrates the four possible combinations:
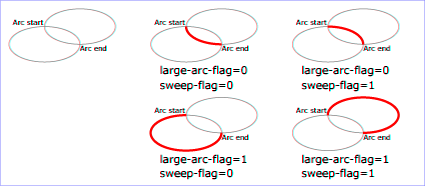
By default, the value of arcpath is 0 (large-arc-flag=0, sweep-flag=1).
Example
See the examples for the SVG_New_path command.