Privilégios
Proteger dados enquanto permitir acesso rápido e fácil para usuários autorizados é um desafio importante para aplicações web. A arquitetura de segurança ORDA é implementada no cerne do seu datastore e permite que você defina privilégios específicos para todas as sessões de usuário para os vários recursos no seu projeto (datastore, dataclasses, funções, etc.).
Visão Geral
A arquitetura de segurança da ORDA é baseada nos conceitos de privilégios, ações de permissão (ler, criar, etc.) e recursos.
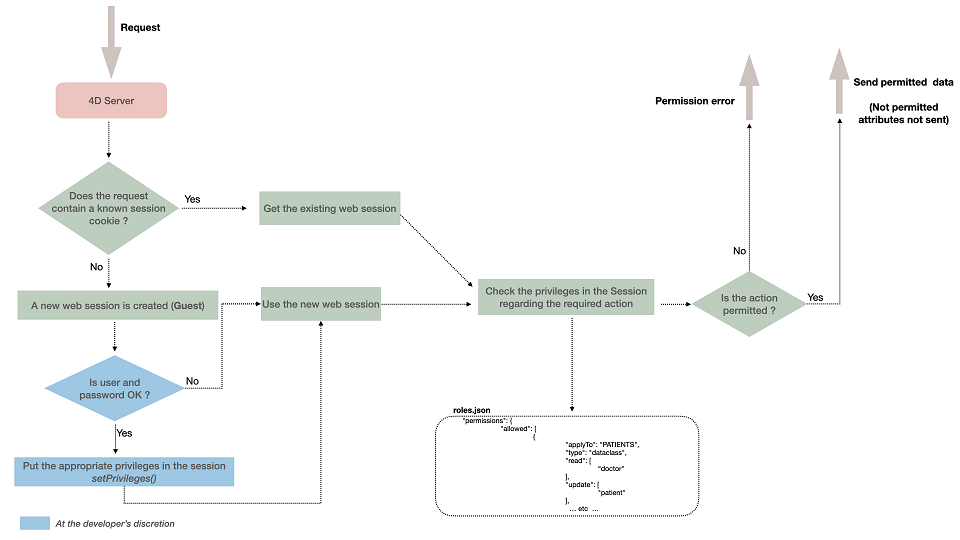
Quando os usuários são registrados, sua sessão é automaticamente carregada com os privilégios associados. Os privilégios são atribuídos à sessão usando a função session.setPrivileges().
Cada solicitação de usuário enviada na sessão é avaliada em relação aos privilégios definidos no arquivo roles.json do projeto.
Se um usuário tentar executar uma ação e não tiver os direitos de acesso adequados, um erro de privilégio é gerado ou, no caso de falta de permissão de leitura nos atributos, eles não são enviados.
Resources
You can assign specific permission actions to the following resources in your project:
- o datastore
- uma classe de dados
- um atributo (inclusive calculado e aliases)
- uma função de classe de modelo de dados
Each time a resource is accessed within a session (whatever the way it is accessed), 4D checks that the session has the appropriate permissions, and rejects the access if it is not authorized.
Uma ação de permissão definida em um determinado nível é herdada por padrão em níveis inferiores, mas várias permissões podem ser configuradas:
- Uma ação de permissão definida no nível do datastore é automaticamente atribuída a todas as dataclasses.
- Uma ação de permissão definida ao nível da classe de dados substitui a definição do armazenamento de dados (se existir). Por padrão, todos os atributos do dataclass herdam das permissões de banco de dados.
- Ao contrário das permissões da classe de dados, uma ação de permissão definida no nível do atributo não substitui a(s) permissão(ões) pai da classe de dados, mas é adicionada a ela. Por exemplo, se você atribuiu o privilégio "geral" a uma classe de dados e o privilégio "detalhe" a um atributo da classe de dados, ambos os privilégios "geral" e "detalhe" devem ser definidos na sessão para acessar o atributo.
Ações de permissão
As ações disponíveis estão relacionadas com o recurso alvo.
| Acções | armazém de dados | dataclass | atributo | função de modelo de dados |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| create | Criar entidade em qualquer classe de dados | Criar entidade nesta classe de dados | Criar uma entidade com um valor diferente do valor padrão permitido para este atributo (ignorado para atributos alias). | n/a |
| read | Ler atributos em qualquer dataclass | Ler atributos nesta classe de dados | Leia o conteúdo desse atributo | n/a |
| update | Atualizar atributos em qualquer classe de dados. | Atualiza os atributos nesta classe de dados. | Atualiza o conteúdo deste atributo (ignorado para atributos alias). | n/a |
| drop | Eliminar dados em qualquer classe de dados. | Eliminar dados nesta classe de dados. | Excluir um valor não nulo para este atributo (exceto para alias e atributo calculado). | n/a |
| execute | Executar qualquer função no projeto (datastore, dataclass, seleção de entidade, entidade) | Executa qualquer função na classe de dados. Funções de Dataclass e funções de seleção de entidades, e funções de seleção de entidades são tratadas como funções de dataclass | n/a | Executar esta função |
| describe | Todas as classes de dados estão disponíveis na /rest/$catalog API | Esta dataclass está disponível na API /rest/$catalog | Esse atributo está disponível na API /rest/$catalog. | Esta função de classe de dados está disponível na API /rest/$catalog |
| promote | n/a | n/a | n/a | Associa um determinado privilégio durante a execução da função. O privilégio é temporariamente adicionado à sessão e removido no final da execução da função. Por segurança, só o processo de execução da função é acrescentado o privilégio, não toda a sessão. |
Notas:
- Um alias pode ser lido assim que os privilégios de sessão permitir o acesso ao alias em si, Mesmo que os privilégios de sessão não permitam o acesso aos atributos que resolvem o alias.
- Um atributo calculado pode ser acessado mesmo que não haja permissões sobre os atributos sobre os quais ele é construído.
- Valores padrão: na implementação atual, apenas Null está disponível como valor padrão.
A definição das permissões deve ser coerente, nomeadamente:
- As permissões update e drop também precisam de permissão read (mas create não precisa)
- promover a permissão também precisa descrever a permissão.
Privilégios e funções
Um privilégio é a capacidade técnica de executar ações em recursos, enquanto uma função é um privilégio estabelecido para ser usado por um administrador. Basicamente, uma função reúne vários privilégios para definir um perfil de usuário corporativo. Por exemplo, "manageInvoices" poderia ser um privilégio enquanto "secretary" poderia ser uma função (que inclui "manageInvoices" e outros privilégios).
Um privilégio ou um papel pode ser associado a várias combinações de "ação + recurso". Podem ser associados vários privilégios a uma ação. Um privilégio pode incluir outros privilégios.
-
Você cria privilégios e/ou funções no arquivo
roles.json(veja abaixo). Você configurou o escopo dele, atribuindo-lhes a ação de permissão aplicada aos recursos. -
Você concede privilégios e/ou funções a cada sessão de usuário usando o método
.setPrivileges()da classeSession.
Exemplo
Para permitir uma função em uma sessão:
exposed Function authenticate($identifier : Text; $password : Text)->$result : Text
var $user : cs. UsersEntity
Session.clearPrivileges()
$result:="Your are authenticated as Guest"
$user:=ds. Users.query("identifier = :1"; $identifier).first()
If ($user#Null)
If (Verify password hash($password; $user.password))
Session.setPrivileges(New object("roles"; $user.role))
$result:="Your are authenticated as "+$user.role
End if
End if
ficheiro roles.json
O arquivo roles.json descreve todas as configurações de segurança do projeto.
Em um contexto diferente de Qodly (cloud), é necessário criar esse arquivo no seguinte local: <project folder>/Project/Sources/. Ver a seção Arquitetura.
A sintaxe do ficheiro roles.json é a seguinte:
| Nome da propriedade | Tipo | Obrigatório | Descrição | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| privileges | Coleção de objectos privilege | X | Lista de privilégios definidos | ||
| [].privilege | Text | Nome do privilégio | |||
| [].includes | Coleção de strings | Lista de nomes de privilégios incluídos | |||
| roles | Coleção de objetos role | Lista de roles definidos | |||
| [].role | Text | Nome da role | |||
| [].privileges | Coleção de strings | Lista de nomes de privilégios incluídos | |||
| permissions | Object | X | Lista de acções permitidas | ||
| allowed | Coleção de objectos permission | Lista de permissões permitidas | |||
| [].applyTo | Text | X | Nome do recurso alvo | ||
| [].type | Text | X | Tipo de recurso: "datastore", "dataclass", "attribute", "method" | ||
| [].read | Coleção de strings | Lista de privilégios | |||
| [].create | Coleção de strings | Lista de privilégios | |||
| [].update | Coleção de strings | Lista de privilégios | |||
| [].drop | Coleção de strings | Lista de privilégios | |||
| [].describe | Coleção de strings | Lista de privilégios | |||
| [].execute | Coleção de strings | Lista de privilégios | |||
| [].promote | Coleção de strings | Lista de privilégios |
- O nome do privilégio "WebAdmin" está reservado à aplicação. Não se recomenda a utilização deste nome para privilégios personalizados.
- Os nomes
privilegeserolesnão diferenciam maiúsculas de minúsculas.
Atribuição de permissões a funções da classe ORDA
Ao configurar as permissões, as funções de classe ORDA são declaradas no elemento applyTo usando a seguinte sintaxe:
<DataclassName>.<functionName>
For example, if you want to apply a permission to the following function:
// cs.CityEntity class
Class extends Entity
Function getPopulation() : Integer
...
... você precisa escrever:
"applyTo":"City.getPopulation"
It means that you cannot use the same function names in the various ORDA classes (entity, entity selection, dataclass) if you want them to be assigned privileges. In this case, you need to use distinct function names. Por exemplo, se você tiver criado uma função "drop" nas classes cs.CityEntity e cs.CitySelection, precisará dar a elas nomes diferentes, como dropEntity() e dropSelection(). Em seguida, você pode escrever no arquivo "roles.json":
"permissions": {
"allowed": [
{
"applyTo": "City.dropEntity",
"type": "method",
"promote": [
"name"
]
},
{
"applyTo": "City.dropSelection",
"type": "method",
"promote": [
"name"
]
}
]
Arquivo Roles_Errors.json
O arquivo roles.json é analisado por 4D na inicialização. Você precisa reiniciar o aplicativo se quiser que as modificações neste arquivo sejam consideradas.
Em caso de erro(s) ao analisar o arquivo roles.json, 4D carrega o projeto, mas desabilita a proteção de acesso global - isso permite ao desenvolvedor acessar os arquivos e corrigir o erro. Um arquivo de erro chamado Roles_Errors.json é gerado na pasta Logs do projeto e descreve a(s) linha(s) de erro. Este arquivo é automaticamente excluído quando o arquivo roles.json não contém mais erro(s).
Recomenda-se verificar na inicialização se existe um arquivo Roles_Errors.json na pasta Logs, o que significa que houve um erro de análise e que os acessos não serão limitados. Pode escrever, por exemplo:
If (Not(File("/LOGS/"+"Roles_Errors.json").exists))
…
Else // you can prevent the project to open
ALERT("The roles.json file is malformed or contains inconsistencies, the application will quit.")
QUIT 4D
End if
Inicialização de privilégios para implantação
Por padrão, se nenhum parâmetro específico for definido no arquivo roles.json, os acessos não serão limitados. Essa configuração permite que você desenvolva a aplicação sem ter que se preocupar com os acessos.
No entanto, quando a aplicação estiver prestes a ser implantado, uma boa prática é bloquear todos os privilégios e, em seguida, configurar o arquivo para abrir apenas as partes controladas para sessões autorizadas. Para bloquear todos os privilégios em todos os recursos, coloque o seguinte arquivo roles.json na pasta do seu projeto (ele inclui exemplos de métodos):
{
"privileges": [
{
"privilege": "none",
"includes": []
}
],
"roles": [],
"permissions": {
"allowed": [{
"applyTo": "ds",
"type": "datastore",
"read": [
"none"
],
"create": [
"none"
],
"update": [
"none"
],
"drop": [
"none"
],
"execute": [
"none"
],
"describe": [
"none"
],
"promote": [
"none"
]
},
{
"applyTo": "ds.loginAs",
"type": "method",
"execute": [
"guest"
]
},
{
"applyTo": "ds.hasPrivilege",
"type": "method",
"execute": [
"guest"
]
},
{
"applyTo": "ds.clearPrivileges",
"type": "method",
"execute": [
"guest"
]
},
{
"applyTo": "ds.isGuest",
"type": "method",
"execute": [
"guest"
]
},
{
"applyTo": "ds.getPrivileges",
"type": "method",
"execute": [
"guest"
]
},
{
"applyTo": "ds.setAllPrivileges",
"type": "method",
"execute": [
"guest"
]
}
]
}
}