Roles and Privileges
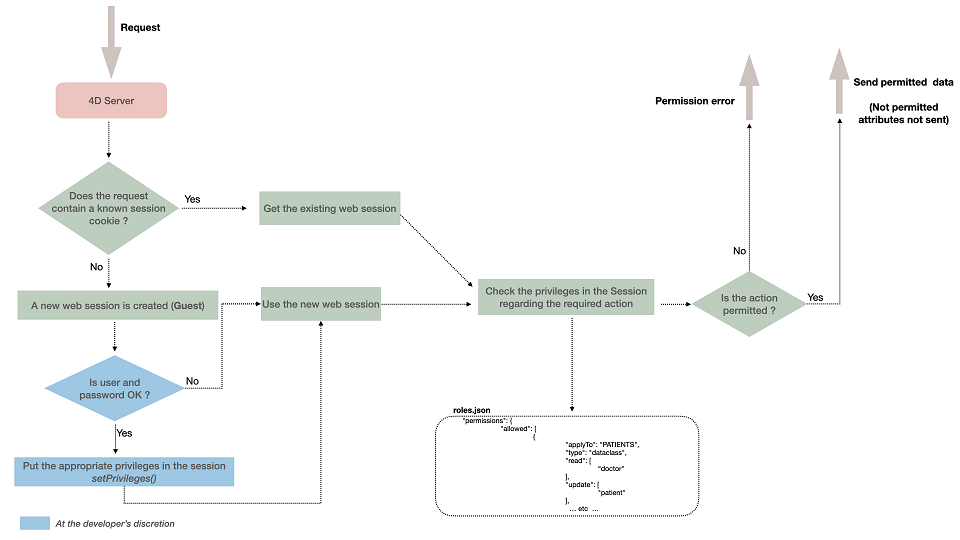
Proteger dados enquanto permitir acesso rápido e fácil para usuários autorizados é um desafio importante para aplicações web. A arquitetura de segurança ORDA é implementada no cerne do seu datastore e permite que você defina privilégios específicos para todas as sessões de usuário da web ou REST para os vários recursos no seu projeto (datastore, dataclasses, funções, etc.).
Visão Geral
A arquitetura de segurança da ORDA é baseada nos conceitos de privilégios, ações de permissão (ler, criar, etc.) e recursos.
Quando os usuários da web ou os usuários do REST fazem login, sua sessão é automaticamente carregada com a(s) privilégio(s) associado(s). Os privilégios são atribuídos à sessão usando a função session.setPrivileges().
Cada solicitação de usuário enviada dentro da sessão é avaliada em relação aos privilégios definidos no arquivo roles.json do projeto.
Se um usuário tentar executar uma ação e não tiver os direitos de acesso adequados, um erro de privilégio é gerado ou, no caso de falta de permissão de leitura nos atributos, eles não são enviados.
Resources
You can assign specific permission actions to the following resources in your project:
- the datastore
- the dataclasses
- attributes (including computed and alias)
- functions of the data model classes
- singleton functions
Each time a resource is accessed within a session (whatever the way it is accessed), 4D checks that the session has the appropriate permissions, and rejects the access if it is not authorized.
Permissions
A permission is the ability to do an action on a resource. For example, execute the ds.myTable.myFunction() represents a permission. Permissions are defined for the project in the roles.json file. Each permission can be given to one or more privileges.
When no specific permission has been defined for a resource, access to the resource may be automatically unrestricted or restricted depending on the default mode defined for the project.
Ações de permissão
As ações disponíveis estão relacionadas com o recurso alvo.
| Acções | armazém de dados | dataclass | atributo | função de modelo de dados ou função singleton |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| create | Criar entidade em qualquer classe de dados | Criar entidade nesta classe de dados | Criar uma entidade com um valor diferente do valor padrão permitido para este atributo (ignorado para atributos alias). | n/a |
| read | Ler atributos em qualquer dataclass | Ler atributos nesta classe de dados | Leia o conteúdo desse atributo | n/a |
| update | Atualizar atributos em qualquer classe de dados. | Atualiza os atributos nesta classe de dados. | Atualiza o conteúdo deste atributo (ignorado para atributos alias). | n/a |
| drop | Eliminar dados em qualquer classe de dados. | Eliminar dados nesta classe de dados. | Excluir um valor não nulo para este atributo (exceto para alias e atributo calculado). | n/a |
| execute | Execute any function on the project (datastore, dataclass, entity selection, entity, singleton) | Executa qualquer função na classe de dados. Funções de Dataclass e funções de seleção de entidades, e funções de seleção de entidades são tratadas como funções de dataclass | n/a | Executar esta função |
| promote | n/a | n/a | n/a | Associa um determinado privilégio durante a execução da função. The privilege is temporary added and removed at the end of the function execution. Por segurança, só o processo de execução da função é acrescentado o privilégio, não toda a sessão. |
- An alias can be read as soon as the session privileges allow the access to the alias itself, even if the session privileges do no allow the access to the attributes resolving the alias.
- A computed attribute can be accessed even if there are no permissions on the attributes upon which it is built.
- Você pode atribuir uma ação de permissão a uma classe de singleton (tipo
singleton), nesse caso ele será aplicado a todas as suas funções expostas, ou a uma função de singleton (tiposingletonMethod). - You can set/remove the promote action dynamically to a web process using the
promote()anddemote()functions. - Valores padrão: na implementação atual, apenas Null está disponível como valor padrão.
- No REST modo de login, a função
authentify()é sempre executável por usuários convidados, independentemente da configuração das permissões.
Setting permissions requires to be consistent, in particular update and drop permissions also need read permission (but create does not need it).
Inherited permissions
Uma ação de permissão definida em um determinado nível é herdada por padrão em níveis inferiores, mas várias permissões podem ser configuradas:
- Uma ação de permissão definida no nível do datastore é automaticamente atribuída a todas as dataclasses. A ação de permissão execute definida no nível de datastore aplica-se a todas as funções do projeto, incluindo todas as funções singleton.
- Uma ação de permissão definida ao nível da classe de dados substitui a definição do armazenamento de dados (se existir). Por padrão, todos os atributos do dataclass herdam das permissões de banco de dados.
- Ao contrário das permissões da classe de dados, uma ação de permissão definida no nível do atributo não substitui a(s) permissão(ões) pai da classe de dados, mas é adicionada a ela. Por exemplo, se você atribuiu o privilégio "geral" a uma classe de dados e o privilégio "detalhe" a um atributo da classe de dados, ambos os privilégios "geral" e "detalhe" devem ser definidos na sessão para acessar o atributo.
Permissões controlam o acesso a objetos ou funções de armazenamento de dados. Se você deseja filtrar os dados lidos de acordo com alguns critérios, você pode considerar restringir as seleções de entidades que pode ser mais apropriado neste caso.
Atribuição de permissões a funções da classe ORDA
When configuring permissions, ORDA class functions are declared in the applyTo element using the following syntax:
<DataclassName>.<functionName>
For example, if you want to apply a permission to the following function:
// cs.CityEntity class
Class extends Entity
Function getPopulation() : Integer
...
... você precisa escrever:
"applyTo":"City.getPopulation"
It means that you cannot use the same function names in the various ORDA classes (entity, entity selection, dataclass) if you want them to be assigned privileges. In this case, you need to use distinct function names. For example, if you have created a "drop" function in both cs.CityEntity and cs.CitySelection classes, you need to give them different names such as dropEntity() and dropSelection(). Em seguida, você pode escrever no arquivo "roles.json":
"permissions": {
"allowed": [
{
"applyTo": "City.dropEntity",
"type": "method",
"promote": [
"name"
]
},
{
"applyTo": "City.dropSelection",
"type": "method",
"promote": [
"name"
]
}
]
Privilégios e funções
Um privilégio é a habilidade técnica de executar ações em recursos, enquanto um cargo é um privilégio posto de uso por um administrador. Basicamente, uma função reúne vários privilégios para definir um perfil de usuário corporativo. Por exemplo, "manageInvoices" poderia ser um privilégio enquanto "secretary" poderia ser uma função (que inclui "manageInvoices" e outros privilégios).
Um privilégio ou um papel pode ser associado a várias combinações de "ação + recurso". Podem ser associados vários privilégios a uma ação. Um privilégio pode incluir outros privilégios.
-
Você cria privilégios e/ou funções no arquivo
roles.json(veja abaixo). Você configurou o escopo dele, atribuindo-lhes a ação de permissão aplicada aos recursos. -
Você permite privilégios e/ou funções para cada sessão usuário usando a função
.setPrivileges()da classeSession.
Exemplo
Para permitir uma função em uma sessão:
exposed Function authenticate($identifier : Text; $password : Text)->$result : Text
var $user : cs.UsersEntity
Session.clearPrivileges()
$result:="Você está autenticado como Convidado"
$user:=ds.Users.query("identifier = :1"; $identifier).first()
If ($user#Null)
If (Verify password hash($password; $user.password))
Session.setPrivileges(New object("roles"; $user.role))
$result:="Você está autenticado como "+$user.role
End if
End if
arquivo roles.json
The roles.json file describes the whole web security settings for the project. A sintaxe do arquivo roles.json é a seguinte:
| Nome da propriedade | Tipo | Obrigatório | Descrição | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| privileges | Coleção de objetos de 'privilégio' | X | Lista de privilégios definidos | ||
| [].privilege | Text | Nome do privilégio | |||
| [].includes | Coleção de strings | Lista de nomes de privilégios incluídos | |||
| roles | Coleção de objetos papel | Lista de roles definidos | |||
| [].role | Text | Nome da role | |||
| [].privileges | Coleção de strings | Lista de nomes de privilégios incluídos | |||
| permissions | Object | X | Lista de acções permitidas | ||
| allowed | Colección de objetos permission | Lista de permissões permitidas | |||
| [].applyTo | Text | X | Targeted resource name | ||
| [].type | Text | X | Tipo de recurso: "datastore", "dataclass", "attribute", "method", "singletonMethod", "singleton" | ||
| [].read | Coleção de strings | Lista de privilégios | |||
| [].create | Coleção de strings | Lista de privilégios | |||
| [].update | Coleção de strings | Lista de privilégios | |||
| [].drop | Coleção de strings | Lista de privilégios | |||
| [].execute | Coleção de strings | Lista de privilégios | |||
| [].promote | Coleção de strings | Lista de privilégios | |||
| restrictedByDefault | Parâmetros | If true, access to resources without explicit permissions is denied | |||
| forceLogin | Parâmetros | If true, enables "forceLogin" mode |
- O nome do privilégio "WebAdmin" está reservado à aplicação. Não se recomenda a utilização deste nome para privilégios personalizados.
privilegesandrolesnames are case-insensitive.
Default File Location and Content
When a new project is created, a default roles.json file is generated at:
<project folder>/Project/Sources/
Ver la sección Arquitectura.
Default content:
{
"privileges": [
],
"roles": [
],
"permissions": {
"allowed": [
{
"applyTo": "ds",
"type": "datastore",
"read": [],
"create": [],
"update": [],
"drop": [],
"execute": [],
"promote": []
}
]
},
"restrictedByDefault": false,
"forceLogin": false
}
Em versões anteriores, o arquivo roles.json não foi criado por padrão. A partir de 4D 20 R6, ao abrir um projeto existente que não contém um cargos. arquivo son ou as configurações "forceLogin": true, a Ativar autenticação REST através de d. Função uthentify() está disponível na página Recursos Web da caixa de diálogo Configurações. Este botão atualiza automaticamente suas configurações de segurança (você pode ter que modificar seu código, veja este post de blog).
In Qodly Studio for 4D, the login mode can be set using the Force login option in the Roles and Privileges panel.
Restriction Modes
The restrictedByDefault property configures how every resource are accessed when no specific permission is defined for it:
- Unrestricted mode (
restrictedByDefault: false): Resources without defined permissions are accessible to all requests. This mode is suitable for development environments where access can be gradually restricted. - Restricted mode (
restrictedByDefault: true): Resources without defined permissions are blocked by default. This mode is recommended for production environments where access must be explicitly granted.
- When creating a new project, the
restrictedByDefaultproperty is set to false in the roles.json file (see below). Keep in mind that this configuration is tailored for quick start and smooth development. In production environment, it is recommended to set therestrictedByDefaultandforceLoginproperties to true. - In projects converted from previous releases; when enabling access to Qodly Studio using the One-click configuration dialog, the
restrictedByDefaultproperty is added with value true in the roles.json file.
Recommended Configuration
Depending on your environment, the recommended settings are:
- Production: Set both
restrictedByDefaultandforceLoginto true. This ensures maximum security by requiring user authentication and explicitly defined permissions for resource access. - Development: Set both
restrictedByDefaultandforceLoginto false. This allows easier access during development and debugging, with the possibility to gradually apply restrictions.
Arquivo Roles_Errors.json
O arquivo roles.json é analisado pelo 4D na inicialização. Você precisa reiniciar o aplicativo se quiser que as modificações neste arquivo sejam consideradas.
Em caso de erro(s) ao analisar o arquivo roles.json, o 4D carrega o projeto, mas desabilita a proteção de acesso global - isso permite ao desenvolvedor acessar os arquivos e corrigir o erro. Um arquivo de erro chamado Roles_Errors.json é gerado na pasta Logs do projeto e descreve a(s) linha(s) de erro. Este arquivo é automaticamente excluído quando o arquivo roles.json não contém mais erro(s).
Se recomienda comprobar al inicio si existe un archivo Roles_Errors.json en la carpeta Logs, lo que significa que se ha producido un error de análisis y que los accesos no estarán limitados. Pode escrever, por exemplo:
Se (Not(File("/LOGS/"+"Roles_Errors.json").exists))
…
Senão // você pode impedir o projeto de abrir
ALERT("Os papéis. arquivo filho está malformado ou contém inconsistências, o aplicativo será encerrado.")
QUIT 4D
Finalizado, se
Exemplo de configuração de privilégios
{
"forceLogin": true,
"restrictedByDefault": true,
"permissions": {
"allowed": [
{
"applyTo": "People",
"type": "dataclass",
"read": [
"viewPeople"
]
}
]
},
"privileges": [
{
"privilege": "viewPeople",
"includes": []
}
],
"roles": []
}